What is a High-Ratio Mortgage and why are rates lower?
September 15, 2025 | Posted by: Patrick Mulhern
What is a High-Ratio Mortgage and Why Are Rates Lower?Can’t believe how much houses cost these days? With prices climbing across Canada, saving for a traditional 20% down payment feels impossible for many. That’s why high-ratio mortgages are becoming so popular – they let you buy a home with less money up front. But here’s the kicker: these mortgages, where you actually pay less initially, often come with lower interest rates. Why? This blog will break down high-ratio mortgages in Canada, explaining how they work, who’s eligible, and why those seemingly backwards interest rates exist. What Is a High-Ratio Mortgage?Essentially, a high-ratio mortgage means you’re putting down less than 20% on a property. This makes the loan itself a bigger chunk of the home’s value – that’s called the Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio. If your LTV is over 80%, you need to get mortgage insurance from either the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC), Sagen, or Canada Guaranty. If you are unable to make your payments, this insurance protects the lender, not you. The opposite is true for a traditional mortgage. Mortgage insurance is not required for down payments of 20% or greater. The idea is simple: with a bigger down payment, you’re less likely to default, so the bank isn’t as worried. Think saving a 20% down payment is a pipe dream? A high LTV mortgage in Canada could be your ticket to owning a home. How High-Ratio Mortgages Work in PracticeOkay, let’s walk through getting a CMHC-insured mortgage, or one from Sagen or Canada Guaranty:
Here’s an example: say you’re buying a $600,000 house and putting 10% down ($60,000). That means you need a $540,000 mortgage. If the insurance premium is 4%, that adds $21,600 to your loan. So, your total original mortgage amount becomes $561,600. And don’t forget, these fees don’t exclude you from first-time homebuyer programs and incentives. Why Are High-Ratio Mortgage Rates Lower?So, why are high-ratio mortgage rates usually lower than regular mortgage rates? It all comes down to risk, or more specifically, the lender’s reduced risk.
Here’s a quick comparison: 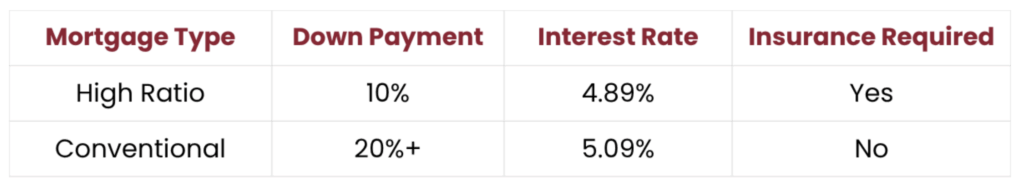 Keep in mind these rates are just examples. Real rates depend on the market, the lender, and your specific situation. Talk to a mortgage pro for personalized rates. Role of High-Ratio Mortgage InsuranceImportant: mortgage insurance from CMHC, Sagen, and Canada Guaranty protects the lender, not you. But it’s thanks to this insurance that you can buy a home with a smaller down payment. The size of your down payment (the loan-to-value ratio) determines the cost of the insurance. A higher LTV and a higher premium are associated with a lesser down payment. This charge is added to your mortgage when you make a single payment. Also, heads up, some provinces charge sales tax on this premium. Before you jump in, get your finances sorted. Our article, Steps to Take Before Applying for a Mortgage, has some great tips. Knowing your credit score, debt situation, and savings will make the process smoother. Who Typically Uses High-Ratio Mortgages?For a few important groups, high-ratio mortgages are an excellent choice:
If you’re in any of these situations, take your credit score seriously! Learn How to Improve Your Credit Score for a Mortgage. You can save a lot of money on interest with even a minor improvement. Pros of High-Ratio Mortgages
Thinking about a fixed or variable rate? Figuring out if fluctuating rates might lead to financial difficulties? Our breakdown on fixed-rate vs. variable-rate mortgages can ease your fears. Cons of High-Ratio Mortgages
It’s equally important to balance the advantages and disadvantages. Our blog post on Avoiding Common Mortgage Mistakes can provide you with clarity. High Ratio vs. Conventional Mortgages: Side-by-SideThe essential differences in these loans can be seen in the side-by-side below: How to Qualify for a High Ratio Mortgage To get a high ratio mortgage, you need to meet the standards set by the insurer and the lender, which require:
Be prepared for “stress testing” – they’ll see if you can still afford your payments if rates go up. Getting pre-approved helps to give you a clear financial picture. Look at your credit scores and learn how they influence you: The Impact of Credit Scores on Mortgage Rates. Final Thoughts: Is a High Ratio Mortgage Right for You?A high ratio mortgage can open doors to homeownership, just keep in mind that it may not be right for everyone. While these loans may seem cheaper at first glance, the costs associated with having them can be higher in the long term. Choose a high-ratio mortgage when:
But most importantly, if in doubt, seek help from qualified mortgage experts in understanding and determining if a high-interest loan makes sense for you. |
.png)